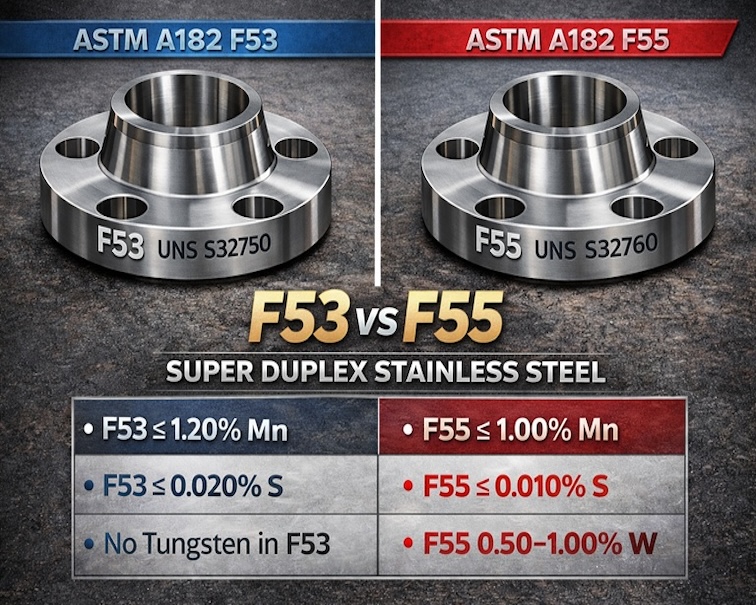
Super Duplex Stainless steel UNS S32750 VS S32760
Super Duplex Stainless Steel refers to the dual-phase austenite and ferrite phases stainless steels,having exceptionally high strength and superior corrosion resistance—especially against pitting, crevice corrosion, and stress-corrosion cracking in chloride enviorement.
Comparing with Duplex stainless steels,Super Duplex stainless steel has higer pitting resistance equivalence number, PREN = %Cr + 3.3 %Mo + 16 %N.
Standard duplex (PREN range: 28–38)Typically Grade EN 1.4462 (also called 2205).
The industry specification NACE MR1075 and Norsok M650 require the three main super duplex stainless steels (Ferralium 255, UNS S32750 and UNS S32760) to have a PREN >40.
S32750 and S32760 are both common grade of Super Duplex stainless steel.Can S32750 replace S32760?
In this page,you can find the answer and the difference between those 2 grade?
1. Chemical Composition of UNS S32750 and S32760
| Element | F53 (UNS S32750) | F55 (UNS S32760) |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | ≤ 0.030 wt % | ≤ 0.030 wt % |
| Manganese (Mn) | ≤ 1.20 wt % | ≤ 1.00 wt % |
| Phosphorus (P) | ≤ 0.035 wt % | ≤ 0.030 wt % |
| Sulfur (S) | ≤ 0.020 wt % | ≤ 0.010 wt % |
| Silicon (Si) | ≤ 0.80 wt % | ≤ 1.00 wt % |
| Chromium (Cr) | 24.00–26.00 wt % | 24.00–26.00 wt % |
| Nickel (Ni) | 6.00–8.00 wt % | 6.00–8.00 wt % |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 3.00–5.00 wt % | 3.00–4.00 wt % |
| Copper (Cu) | ≤ 0.50 wt % | 0.50–1.00 wt % |
| Nitrogen (N) | 0.24–0.32 wt % | 0.20–0.30 wt % |
| Tungsten (W) | — | 0.50–1.00 wt % |
F53 features a molybdenum content range of 3.00 – 5.00%, whereas F55 has a narrower range of 3.00 – 4.00%. This molybdenum content is crucial for improving the metal’s resistance to specific types of corrosion. S32760 is very similar to S32750, but also includes small additions of both copper and tungsten which are suggested to improve corrosion resistance in certain environments.
Nitrogen Content
F53 contains slightly higher nitrogen levels (0.24 – 0.32%) compared to F55 (0.20 – 0.30%). Nitrogen helps boost the alloy’s strength and its resistance to corrosion in specific areas.
Sulfur Content
The maximum sulfur content in F53 is 0.020%, while F55 has a stricter limit of 0.010%. Lower sulfur levels in F55 reduce the risk of intergranular corrosion and enhance its overall corrosion resistance.
Manganese Content
F53 allows for a higher manganese content (up to 1.20%) compared to F55 (up to 1.00%). Manganese plays a role in improving the alloy’s toughness and strength.
2. Mechanical Properties
| Property | F53 (UNS S32750) | F55 (UNS S32760) |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | ≥ 800 MPa (sizes ≤ 50 mm) ≥ 730 MPa (sizes > 50 mm) | 930 MPa |
| Yield Strength | ≥ 550 MPa (≤ 50 mm) ≥ 515 MPa (> 50 mm) | 690 MPa |
| Elongation | ≥ 30 % | ≥ 35 % |
| Hardness | ≤ 310 HB | ~270HB |
3,Typical Applications
- F53: General super-duplex service—oil & gas piping, heat exchangers, chemical processing equipment.
- F55: More demanding, high‐performance service—deepwater subsea systems, aggressive chloride or sour environments,
4,Which one to Choose?
- Cost-preferred, high-corrosion: F53 is widely available in the market and easy to get the material
- Extreme conditions (higher pressures, more aggressive media): F55’s elevated mechanicals and corrosion resistance make it the superior choice—at a higher material cost.and sometimes not easy to have the material in the market.
Both ASTM A182 F53 and F55 super duplex stainless steels provide excellent strength and corrosion resistance for demanding industrial applications. F53 is widely used for general offshore and chemical service, while F55 offers enhanced protection against pitting and crevice corrosion, making it the preferred choice for severe seawater and subsea environments.
Can we use UNS S32750 to replace UNS S32760?
UNS S32750 vs UNS S32760 Super Duplex Stainless Steel Substitution Guide
UNS S32750 (ASTM A182 F53) and UNS S32760 (ASTM A182 F55) are both super duplex stainless steels widely used in offshore, oil & gas, subsea, desalination, and chemical processing applications.
While they are similar in strength and base chemistry, S32750 cannot always replace S32760, especially in severe seawater and subsea environments.
Quick Answer (Engineering Summary)
✅ YES, S32750 can replace S32760
➡ In less aggressive environments and when project specifications allow
❌ NO, S32750 should NOT replace S32760
➡ In critical offshore, subsea, or high-chloride seawater service
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
| Environment | S32750 | S32760 |
|---|---|---|
| Chloride SCC | Excellent | Excellent+ |
| Seawater | Very Good | Excellent |
| Subsea service | Limited approval | Preferred |
| Pitting / Crevice corrosion | Very Good | Superior |
| PREN value (approx.) | ~40 | ~42–45 |
📌 Higher PREN = better corrosion resistance
S32760 consistently performs better in severe marine exposure.
UNS S32750 can replace UNS S32760 only in selected applications, where corrosion severity is lower and project specifications permit substitution. While both super duplex stainless steels offer high strength, UNS S32760 provides superior corrosion resistance, especially in seawater and subsea environments, due to its tungsten alloying.
Product available in UNS S32750 and S32760
UNS S32750 and S32760 Steel Plate
UNS S32750 Flanges and S32760 Flanges
UNS S32750 and S32760 Pipes
UNS S32750 and S32760 Round Bar