ASTM A182 / A182M – Standard Specification for Forged or Rolled Alloy and Stainless Steel Pipe Flanges, Forged Fittings, and Valves and Parts for High-Temperature Service
Download ASTM A182 2024 pdf
ASTM A182 covers:
- Forged or rolled alloy steel materials
- For use in pressure systems and high-temperature services
- Commonly applied in:
- Petrochemical plants
- Oil & gas processing
- Power generation (thermal, nuclear)
- Marine and offshore industries
ASTM A182 Flange Types Available
ASTM A182 alloy steel flanges are manufactured in compliance with:
- ASME B16.5 (sizes up to 24″)
- ASME B16.47 (for larger diameters)
- Pressure Classes: 150#, 300#, 600#, 900#, 1500#, 2500#
Available types:
- Weld Neck Flange (WN)
- Blind Flange (BL)
- Slip-On Flange (SO)
- Socket Weld Flange (SW)
- Threaded Flange (TH)
- Lap Joint Flange (LJ)
- Orifice Flanges
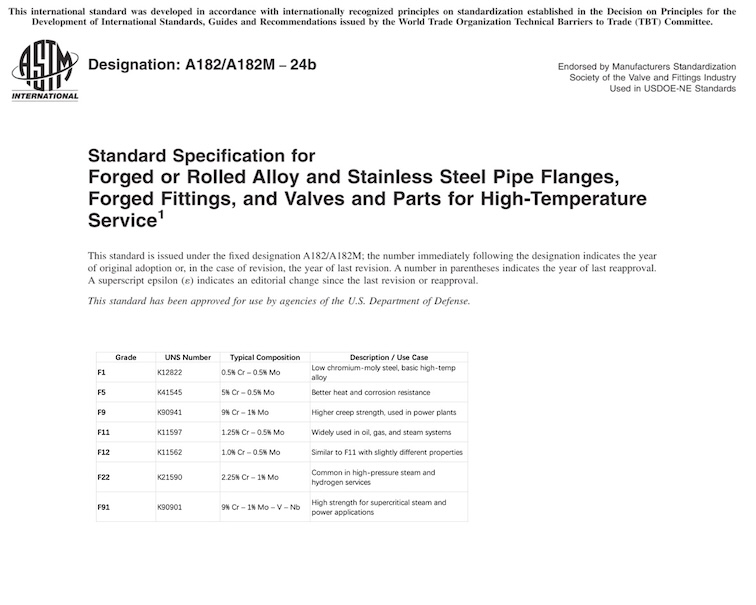
ASTM A182 Low Alloy Steel Grades
| Grade | UNS Number | Typical Composition | Description / Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| ASTM A182 F1 | K12822 | 0.5% Cr – 0.5% Mo | Low chromium-moly steel, basic high-temp alloy |
| F5 | K41545 | 5% Cr – 0.5% Mo | Better heat and corrosion resistance |
| F9 | K90941 | 9% Cr – 1% Mo | Higher creep strength, used in power plants |
| F11 | K11597 | 1.25% Cr – 0.5% Mo | Widely used in oil, gas, and steam systems |
| F12 | K11562 | 1.0% Cr – 0.5% Mo | Similar to F11 with slightly different properties |
| F22 | K21590 | 2.25% Cr – 1% Mo | Common in high-pressure steam and hydrogen services |
| F91 | K90901 | 9% Cr – 1% Mo – V – Nb | High strength for supercritical steam and power applications |
ASTM A182 F1 F5 F9 F11 F12 F22 F91 F92 Flange Manufacture
The low-alloy ferritic steels shall be made by the open-hearth, electric-furnace, or basic-oxygen process with the option of separate degassing and refining processes in each case.
Low Alloy steel heating treatment requirment
| Grade | Heat Treat Type | Austenitizing/Solution Heat Treatment Temperature, Minimum or Range, °F [°C] | Cooling Media | Quenching Cool Below °F [°C] | Tempering Temperature, Minimum or Range, °F [°C] |
| Low Alloy Steels | |||||
| F1 | anneal | 1650 [900] | furnace cool | — | — |
| F5, F5a | normalize and temper | 1650 [900] | air cool | — | 1150 [620] |
| anneal | 1750 [955] | furnace cool | — | — | |
| normalize and temper | 1750 [955] | air cool | — | 1250 [675] | |
| F9 | anneal | 1750 [955] | furnace cool | — | — |
| normalize and temper | 1750 [955] | air cool | — | 1250 [675] | |
| F 91 Types 1 and 2 | normalize and temper or quench and temper | 1900–1975 [1040–1080] | air cool, accelerated air cool, or liquid | — | 1350–1470 [730–800] |
| F92 | normalize and temper | 1900–1975 [1040–1080] | air cool | — | 1350–1470 [730–800] |
| ASTM A182 F 11, Class 1, 2, 3 | anneal | 1650 [900] | furnace cool | — | — |
| normalize and temper | 1650 [900] | air cool | — | 1150 [620] | |
| F 12, Class 1, 2 | anneal | 1650 [900] | furnace cool | — | — |
| normalize and temper | 1650 [900] | air cool | — | 1150 [620] | |
| normalize and temper | 1750 [955] | air cool | — | 1250 [675] | |
| F 22, Class 1, 3 | anneal | 1650 [900] | furnace cool | — | — |
ASTM A182 Low Alloy steel Chemical Composition
Chemical heat analysis shall be performed and consistent with the chemical composition requirements of Table 1.
Grades that add lead, selenium or other elements to make the material easier machined, it should not be used.
| Grade/Identification Symbol | UNS Designation | Composition, % | ||||||||||
| Carbon | Manganese | Phosphorus | Sulfur | Silicon | Nickel | Chromium | Molybdenum | Niobium | Titanium | Other Elements | ||
| Low Alloy Steels | ||||||||||||
| ASTM A182 F1 | K12822 | 0.28 | 0.60–0.90 | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.15–0.35 | … | … | 0.44–0.65 | … | … | … |
| F 2 | K12122 | 0.05–0.21 | 0.30–0.60 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.10–0.60 | … | 0.50–0.81 | 0.44–0.65 | … | … | … |
| F 5 | K41545 | 0.15 | 0.30–0.60 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 4.0–6.0 | 0.44–0.65 | … | … | … |
| F 5a | K42544 | 0.25 | 0.6 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.50–1.00 | 0.5 | 4.0–6.0 | 0.44–0.65 | … | … | … |
| F 9 | K90941 | 0.15 | 0.30–0.60 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.50–1.00 | … | 8.0–10.0 | 0.90–1.10 | … | … | … |
| F 10 | S33100 | 0.10–0.20 | 0.50–0.80 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 1.00–1.40 | 19.0–22.0 | 7.0–9.0 | … | 0.06–0.10 | … | N 0.03–0.07 |
| F 91 Type 1 | K90901 | 0.08–0.12 | 0.30–0.60 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.10–0.50 | 0.4 | 8.0–9.5 | 0.85–1.05 | 0.06–0.10 | … | V 0.18–0.25 |
| Ti 0.02 | ||||||||||||
| Al 0.025 | ||||||||||||
| Cu 0.01 | ||||||||||||
| F 91 Type 2 | K90901 | 0.08–0.12 | 0.30–0.50 | 0.020 | 0.05 | 0.20–0.40 | 0.20 | 8.0–9.5 | 0.85–1.05 | 0.06–0.10 | 0.01 | N 0.03–0.07 |
| V 0.18–0.25 | ||||||||||||
| Zr 0.01 | ||||||||||||
| Al 0.020 | ||||||||||||
| Cu 0.10 | ||||||||||||
| W 0.05 | ||||||||||||
| Sn 0.01 | ||||||||||||
| As 0.01 | ||||||||||||
| Sb 0.003<sup>E</sup> | ||||||||||||
| N/A ratio, min 1.0 | ||||||||||||
| F 11 | K11597 | 0.05–0.15 | 0.30–0.60 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.50–1.00 | … | 1.00–1.50 | 0.44–0.65 | … | … | … |
| Class 1 | ||||||||||||
| F 11 | K11572 | 0.10–0.20 | 0.30–0.80 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.50–1.00 | … | 1.00–1.50 | 0.44–0.65 | … | … | … |
| Class 2 | ||||||||||||
| F 11 | K11572 | 0.10–0.20 | 0.30–0.80 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.50–1.00 | … | 1.00–1.50 | 0.44–0.65 | … | … | … |
| Class 3 | ||||||||||||
| F 12 | K11562 | 0.05–0.15 | 0.30–0.60 | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.50 max | … | 0.80–1.25 | 0.44–0.65 | … | … | … |
| Class 1 | ||||||||||||
| F 12 | K11564 | 0.10–0.20 | 0.30–0.80 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.10–0.60 | … | 0.80–1.25 | 0.44–0.65 | … | … | … |
| Class 2 | ||||||||||||
| F 21 | K31545 | 0.05–0.15 | 0.30–0.60 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.50 max | … | 2.7–3.3 | 0.80–0.96 | … | 0.015–0.035 | V 0.20–0.30 |
| F 3V | K31830 | 0.05–0.18 | 0.30–0.60 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.1 | … | 2.8–3.2 | 0.90–1.10 | … | … | V 0.20–0.30 |
| F 3VCb | K31390 | 0.10–0.15 | 0.30–0.60 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.1 | 0.25 | 2.7–3.3 | 0.90–1.10 | 0.015–0.070 | 0.015 | 0.001–0.003 |
| V 0.20–0.30 | ||||||||||||
| Cu 0.25 | ||||||||||||
| Ca 0.0005–0.0150 | ||||||||||||
| F 22 | K21590 | 0.05–0.15 | 0.30–0.60 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.5 | … | 2.00–2.50 | 0.87–1.13 | … | … | … |
| Class 1 | ||||||||||||
| F 22 | K21590 | 0.05–0.15 | 0.30–0.60 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.5 | … | 2.00–2.50 | 0.87–1.13 | … | … | … |
| Class 3 | ||||||||||||
Tensile and Hardness Requirements of A182 low alloy steel grade
| Grade Symbol | Tensile Strength, min, ksi [MPa] | Yield Strength, min, ksi [MPa]<sup>B</sup> | Elongation in 2 in. [50 mm] or 4D, min, % | Reduction of Area, min, % | Brinell Hardness Number, HBW, unless otherwise indicated |
| Low Alloy Steels | |||||
| F1 | 70 [485] | 40 [275] | 20 | 30 | 143–192 |
| F2 | 70 [485] | 40 [275] | 20 | 30 | 143–192 |
| F5 | 70 [485] | 40 [275] | 20 | 35 | 143–217 |
| F5a | 90 [620] | 65 [450] | 22 | 50 | 187–248 |
| F9 | 85 [585] | 55 [380] | 20 | 40 | 179–217 |
| F 91 Types 1 and 2 | 90 [620] | 60 [415] | 20 | 40 | 190–248 |
| F92 | 90 [620] | 64 [440] | 20 | 45 | 269 max |
| F 11 Class 1 | 60 [415] | 30 [205] | 20 | 45 | 121–174 |
| F 11 Class 2 | 70 [485] | 40 [275] | 20 | 30 | 143–207 |
| F 11 Class 3 | 75 [515] | 45 [310] | 20 | 30 | 156–207 |
| F 12 Class 1 | 60 [415] | 32 [220] | 20 | 45 | 121–174 |
| F 12 Class 2 | 70 [485] | 40 [275] | 20 | 30 | 143–207 |
| F 22 Class 1 | 60 [415] | 30 [205] | 20 | 35 | 170 max |
ASTM A182 alloy steel F1 F5 F9 F11 F12 F22 F91 F92 Heat treatment
After hot working, forgings shall be cooled to a temperature below 1000 °F [538 °C] prior to heat treating in accordance with the requirements of Table 1.
The low alloy steels and ferritic and martensitic stainless steels shall be heat treated in accordance with the requirements of 7.1 and Table 1. When more than one heat treatment option is listed for a Grade in Table 1, any one of the heat treatments listed shall be performed. The selection of the heat treatment shall be at the manufacturer’s option, unless otherwise stated in the purchase order.
Liquid Quenching
Except as permitted in 7.2.2, for F 1, F 2, and F 3, and when agreed to by the purchaser, liquid quenching followed by tempering shall be permitted provided the temperatures in Table 1 for each grade are used.
- 7.2.1.1 Marking—Parts that are liquid quenched and tempered shall be marked “QT.”
Alternatively, Grade F 1, F 2, and F 12, Classes 1 and 2 may be given a heat treatment of 1200 °F [650 °C] minimum after final hot or cold forming.
Nondestructive Test Requirements of ASTM A182
Hollow forgings of Grades F 91 Types 1 and 2, F 92, F 115, F 122, and F 911, with NPS 4 [DIN 100] and larger, whose finished internal surfaces are not accessible to magnetic particle or liquid penetrant examination, shall be examined by an ultrasonic test in accordance with Practice A388/A388M after all forging, mechanical processing, and heat treatment operations have been completed.
Hollow forgings of Grades F 91 Types 1 and 2, F 92, F 115, F 122, and F 911, with NPS 4 [DIN 100] and larger, whose finished internal surfaces are accessible to magnetic particle or liquid penetrant examination, shall be examined on their internal surfaces by either a magnetic particle test in accordance with Practice A275/A275M or by a liquid penetrant examination in accordance with Test Method E165/E165M, as applicable, after all heat treatment, machining, and other mechanical processing operations are completed.
ASTM A182 Alloy steel flanges Marking Requirements
Each flange is marked with:
- ASTM A182
- Grade (e.g., F22, F11)
- Heat number
- Pressure rating (e.g., 600#)
- Manufacturer’s logo
- Size and schedule
ASTM A182 vs ASME SA182 — What’s the Difference?
- ASTM A182 → Standard Specification for Forged or Rolled Alloy and Stainless Steel Pipe Flanges, Forged Fittings, and Valves and Parts for High-Temperature Service
- ASME SA182 → Boiler & Pressure Vessel Code (BPVC)–qualified material for pressure equipment
| Aspect | ASTM A182 | ASME SA182 |
|---|---|---|
| Governing body | ASTM | ASME BPVC |
| Typical application | General industrial piping | Pressure vessels, boilers, high-pressure applications |
| Material Test Certificate | ASTM format | Mandatory ASME U-stamp format if used in pressure vessel fabrication |
| Certification | Standard inspection | Heat number traceability + ASME inspector acceptance |
| Supplementary requirements | Optional S1–S10 | Often required by ASME Section VIII / B31.3 |
How to Choose between ASTM A182 and ASME SA182
ASME SA182 when:
- Equipment is under ASME Section VIII (Pressure Vessel Code)
- ASME B31.1 / B31.3 high-pressure systems
- Boilers, superheaters, heat exchangers
- Customer specs demand “SA” material
Use ASTM A182 when:
- General industrial piping, flanges, fittings
- Non-code service
- Cost-sensitive projects where ASME certification is not required
Related Products
ASTM A182 F11 Weld neck flanges
ASTM A182 F22 Weld neck flanges
ASTM A182 F5 Weld neck flanges
ASTM A182 F91 Weld neck flanges